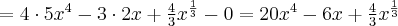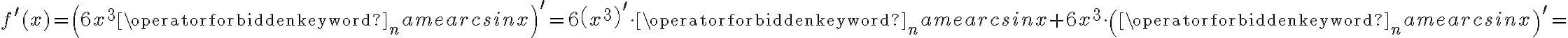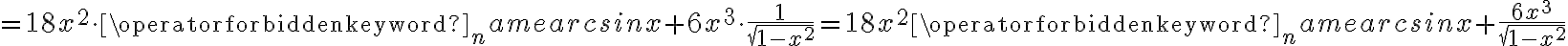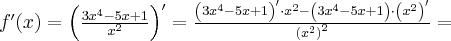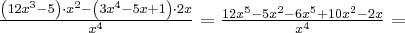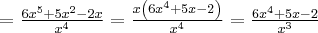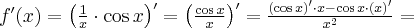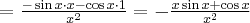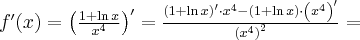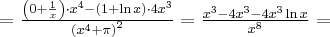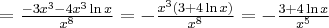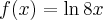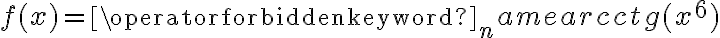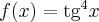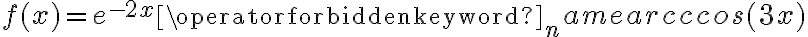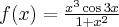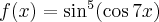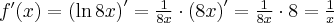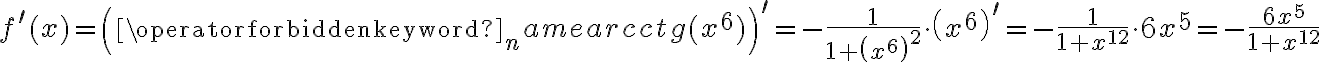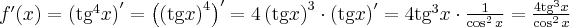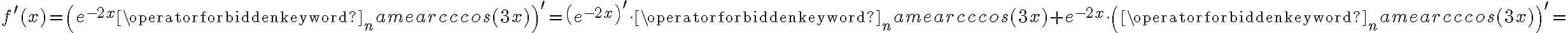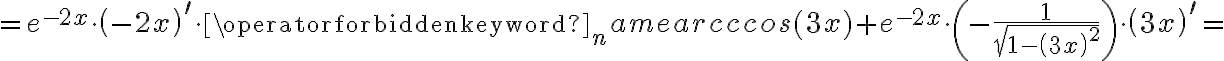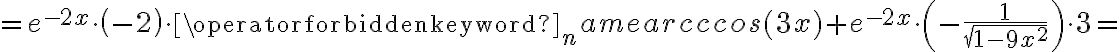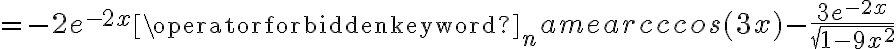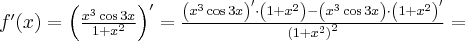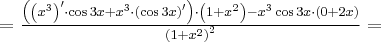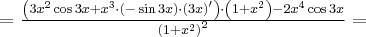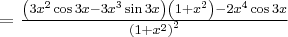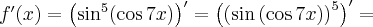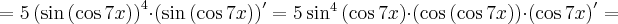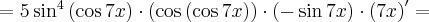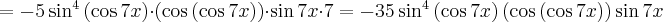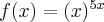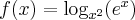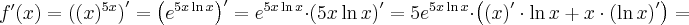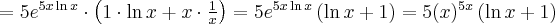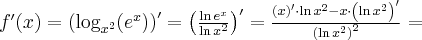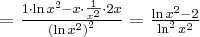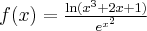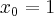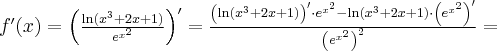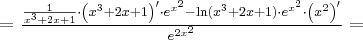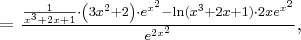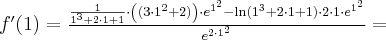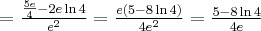Pochodna funkcji jednej zmiennej
1.2 Reguły różniczkowania
Przykłady
1
Korzystając ze wzorów bezpośrednich i praw działań na pochodnych obliczymy pochodne funkcji:
2
Korzystając ze wzorów bezpośrednich i praw działań na pochodnych oraz twierdzenia o pochodnej funkcji złożonej obliczymy pochodne funkcji:
![f(x)=4x^5-3x^2+x\sqrt[3]x-\ln 3 f(x)=4x^5-3x^2+x\sqrt[3]x-\ln 3](https://port.edu.p.lodz.pl/filter/tex/pix.php/4c1597319373d765ab0bcec5bfa92402.png)
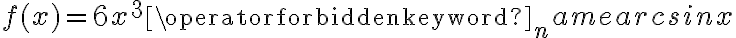
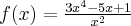
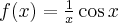

![f^\prime(x)=\left(4x^5-3x^2+x\sqrt[3]x-\ln 3\right)^\prime=4\left(x^5\right)^\prime-3\left(x^2\right)^\prime+\left(x^{\frac43}\right)^\prime-\left(\ln 3\right)^\prime= f^\prime(x)=\left(4x^5-3x^2+x\sqrt[3]x-\ln 3\right)^\prime=4\left(x^5\right)^\prime-3\left(x^2\right)^\prime+\left(x^{\frac43}\right)^\prime-\left(\ln 3\right)^\prime=](https://port.edu.p.lodz.pl/filter/tex/pix.php/514b051c428e523d73f06927e47beccc.png)